- Business & Data Research
- Posts
- Amazon Reviews using NLP (Tensorflow)
Amazon Reviews using NLP (Tensorflow)
Tensorflow, Keras

Natural Language Processing (NLP) is used to analyze and summarize Amazon reviews based on recent studies and comments
Amazon hosts millions of product reviews, which contain rich insights into customer satisfaction, product quality, and user experience. NLP helps automate the understanding of this massive data, enabling:
Better product recommendations
Smarter inventory and marketing decisions
Enhanced customer feedback analysis
Step 1: Importing the required packages
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import nlp
import randomStep 2: Defining the function needed in the beginning itself
def show_history(h):
epochs_trained = len(h.history['loss'])
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(range(0, epochs_trained), h.history.get('accuracy'), label='Training')
plt.plot(range(0, epochs_trained), h.history.get('val_accuracy'), label='Validation')
plt.ylim([0., 1.])
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(range(0, epochs_trained), h.history.get('loss'), label='Training')
plt.plot(range(0, epochs_trained), h.history.get('val_loss'), label='Validation')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def show_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, classes):
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, normalize='true')
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
sp = plt.subplot(1, 1, 1)
ctx = sp.matshow(cm)
plt.xticks(list(range(len(classes))), labels=classes)
plt.yticks(list(range(len(classes))), labels=classes)
plt.colorbar(ctx)
plt.show()
print('Using TensorFlow version', tf.__version__)Step 3: Importing the dataset and using the built-in dataset for practising NLP
amazon_data = pd.read_csv('/content/amazon_reviews.csv', header=None)
amazon_data.head()Step 3.1: Perform the exploratory data analysis
new_header = amazon_data.iloc[0]
amazon_data = amazon_data[1:]
amazon_data.columns = new_header
amazon_data.head()
reviewId userName content score thumbsUpCount reviewCreatedVersion at appVersion
1 032bcafa-54e0-4eb5-9e43-c86f8c5ac5e0 Garry Gordon perfect 5 0 30.14.0.100 2025-08-04 12:33:57 30.14.0.100
2 9109695d-0b7d-48aa-a5a8-232e3978c7be Marcia Chapman you make it EXTREMELY IMPOSSIBLE to find and p... 1 0 30.14.0.100 2025-08-04 11:46:54 30.14.0.100
3 d329bbac-b2e2-40a8-bcec-1dea9aa35233 DominicJ Romero Thanks for sharing 4 0 30.14.0.100 2025-08-04 10:31:01 30.14.0.100
4 c07a7bd2-79f9-4fbf-8599-f7ba1eb0e867 John Hulme bril 5 0 30.14.0.100 2025-08-04 09:35:44 30.14.0.100
5 5a600712-8e68-4334-9cfe-16f275d8ccfe Royce Miller there's no way to talk directly with an agent.... 1 0 30.14.0.100 2025-08-04 09:30:15 30.14.0.100amazon_data.columns
Index(['reviewId', 'userName', 'content', 'score', 'thumbsUpCount',
'reviewCreatedVersion', 'at', 'appVersion'],
dtype='object', name=0)amazon_data.shape
(77129, 8)Step 4: Separate test and training dataset(not used validation test intentionally)
amazon_data_train = amazon_data.sample(frac=0.8, random_state=25)print("No. of training samples: ", amazon_data_train.shape[0])
No. of training samples: 61703amazon_data_test = amazon_data.drop(amazon_data_train.index)print("No. of testing samples: ", amazon_data_test.shape[0])
No. of testing samples: 15426
amazon_data_train['content'].head()
content
27493 The app is ok and to be honest the customer se...
29435 Pretty much done. As Amazon continues to add f...
67392 Amazon has always delivered on time. Returns a...
64456 The crashes I'm unable to open it since yester...
63281 Everytime I search for any book the first opti...
dtype: object
amazon_data_test['content'].head()
content
21 Shes my mistress for christmas
22 buy a lot ,very usefull
23 very easy & convenient
30 Easy ordering and many choices
50 good morning
dtype: objectdef get_review(data):
reviews = [x['text'] for x in data]
return reviewstrain_amazon_reviews = amazon_data_train['content']
test_amazon_reviews = amazon_data_test['content']train_amazon_reviews.iloc[20]
I HATE your new filter. It's slow. It's Not intuitive. It's medevil. It doesn't produce results any better than if i did it on my own. Your search results typically are not even relevant to what I'm looking for. I could pay the neighbor kid five bucks to walk to the store and buy what I need faster. I used to spend 75% of my shopping budget with Amazon but now, I don't even spend 10%. Not the Amazon cares because they aren't responding or doing anything to change.test_amazon_reviews.iloc[30]
Enjoy using appStep 5: Create Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizertokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=10000, oov_token='<UNK>')
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_amazon_reviews.fillna(''))train_amazon_reviews.iloc[0]
The app is ok and to be honest the customer service is great, my issue is the delivery drivers. So many times a package gets delivered to a neighbour or somewhere completely different even though I have put a full description of where my property is and how to get to it, very poor service.lengths_train = [t.split() for t in train_amazon_reviews.fillna('')]
plt.hist([len(t) for t in lengths_train])
plt.show()
max_length = 130
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequencesdef get_sequences(tokenizer, reviews):
sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(reviews)
padded_sequences = pad_sequences(sequences, truncating='post', maxlen=max_length)
return padded_sequencespadded_train_amazon_reviews = get_sequences(tokenizer, train_amazon_reviews.fillna(''))
padded_test_amazon_reviews = get_sequences(tokenizer, test_amazon_reviews.fillna(''))padded_train_amazon_reviews[0]
array([ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 8,
9, 526, 5, 3, 30, 1116, 2, 60, 46, 9, 64,
11, 182, 9, 2, 52, 486, 25, 154, 130, 7, 181,
358, 144, 3, 7, 4651, 31, 1055, 364, 253, 57, 328,
4, 17, 235, 7, 481, 1060, 13, 191, 11, 2967, 9,
5, 128, 3, 27, 3, 6, 59, 427, 46], dtype=int32)padded_test_amazon_reviews[0]
array([ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 11, 1, 12, 666],
dtype=int32)Step 6: Create the labels
train_classes = amazon_data_train['score']
test_classes = amazon_data_test['score']train_classes
score
27493 2
29435 1
67392 5
64456 1
63281 2
... ...
29209 1
8733 4
64237 1
27272 2
41266 1
61703 rows × 1 columns
dtype: objecttest_classes
score
21 5
22 5
23 5
30 5
50 5
... ...
77082 5
77098 1
77105 1
77117 1
77120 1
15426 rows × 1 columns
dtype: objecttrain_classes_numeric = pd.to_numeric(train_classes, errors='coerce').dropna()
plt.hist(train_classes_numeric)
plt.show()
test_classes_numeric = pd.to_numeric(test_classes, errors='coerce').dropna()
plt.hist(test_classes_numeric)
plt.show()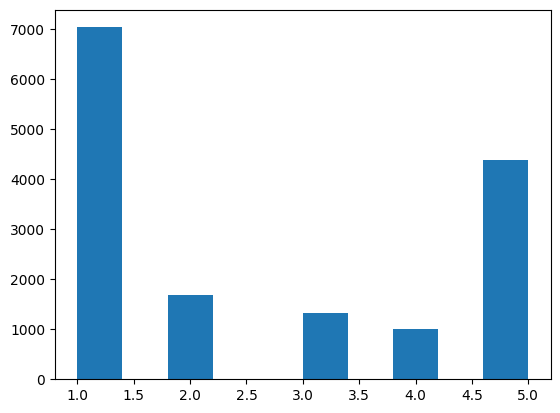
class_to_index = dict((c, i) for i, c in enumerate(set(train_classes_numeric)))
class_to_index
{1: 0, 2: 1, 3: 2, 4: 3, 5: 4}
index_to_class = dict((v, k) for k, v in class_to_index.items())
index_to_class
{0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 4, 4: 5}
Step 7: Create and Train the model
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(10000, 16, input_length=max_length),
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(20, return_sequences=True)),
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(tf.keras.layers.LSTM(20)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation='softmax') # Change to 5 units and softmax for multi-class
])
model.compile(
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', # Change loss for integer labels
optimizer='adam',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
model.summary()Model: "sequential_2"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ embedding_2 (Embedding) │ ? │ 0 (unbuilt) │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ bidirectional_4 (Bidirectional) │ ? │ 0 (unbuilt) │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ bidirectional_5 (Bidirectional) │ ? │ 0 (unbuilt) │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dense_2 (Dense) │ ? │ 0 (unbuilt) │
└─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 0 (0.00 B)
Trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)val_reviews_train = amazon_data_train['score']
val_reviews_train.head()
score
27493 2
29435 1
67392 5
64456 1
63281 2
dtype: objectval_sequence_train = get_sequences(tokenizer, train_amazon_reviews.fillna(''))
val_reviews_train.iloc[0],val_labels_train[0]h = model.fit(
padded_train_amazon_reviews,
val_labels_train,
validation_data=(padded_test_amazon_reviews, test_labels), # Use test_labels instead of test_classes_numeric
epochs=10,
callbacks= [tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=2)]
)show_history(h)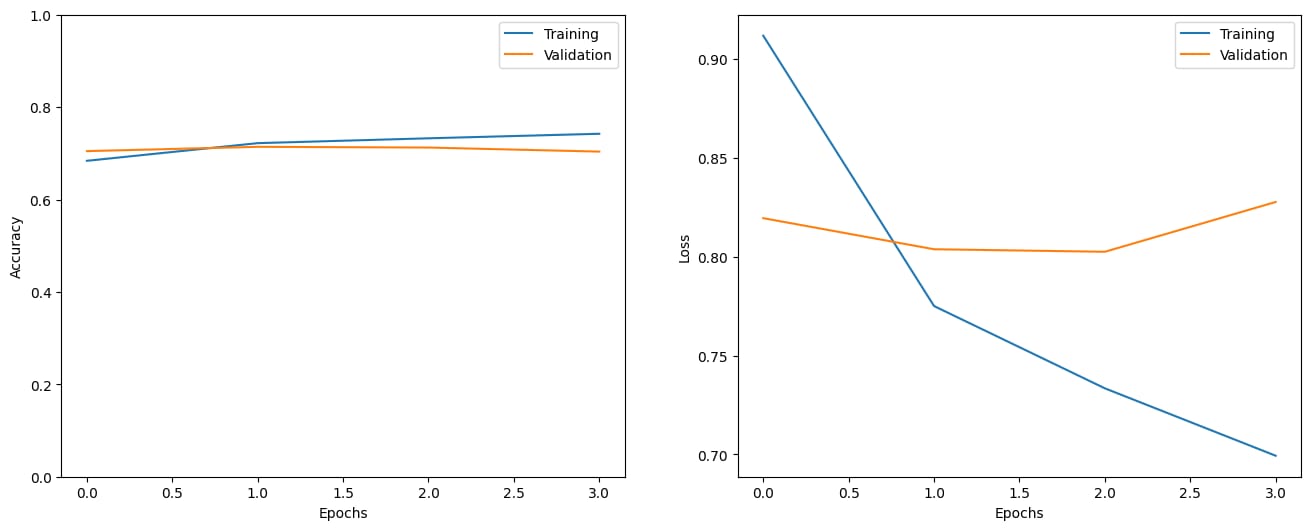
Step8 : Evaluate the Model and Perform a Confusion Matrix
test_reviews = amazon_data_test['content']
test_sequences = get_sequences(tokenizer, test_reviews.fillna(''))
test_labels = np.array([class_to_index[score] for score in test_classes_numeric])_= model.evaluate(test_sequences, test_labels, verbose=0)i = random.randint(0, len(test_reviews) - 1)
print("Review:", test_reviews.iloc[i])
print("Label:", test_labels[i])
p = model.predict(np.expand_dims(test_sequences[i], axis=0))[0]
Review: Amazon is good & fast delivery
Label: 4
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 57ms/stepp = model.predict(single_test_sequence)[0]
print("Predicted probabilities:", p)predicted_class = np.argmax(p)
print("Predicted class:", predicted_class)
Predicted class: 4
show_confusion_matrix(test_labels, np.argmax(model.predict(test_sequences), axis=1), list(class_to_index.keys()))